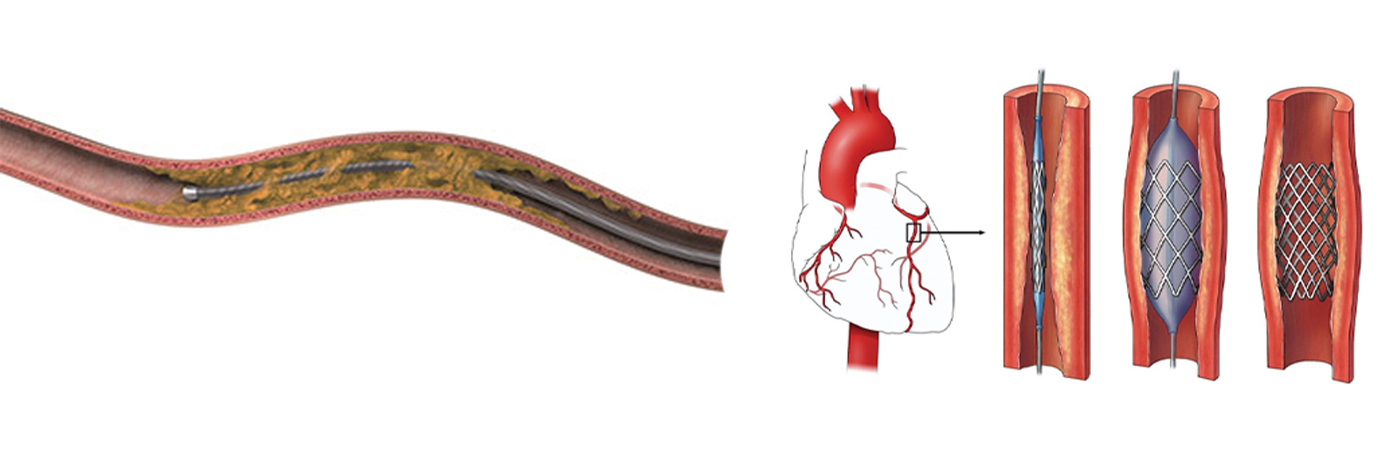
Chronic Total
Chronic total occlusion is a complete or nearly complete blockage of one or more coronary arteries either the left main or right coronary artery. One of the arteries that delivers oxygen-rich blood to your heart has become completely blocked or occluded for three months or longer buildup of plaque within a coronary artery. When this happens, blood flow to the heart is compromised. CTO is a common heart disorder in patients with coronary artery disease.Between 20 and 25 percent of patients with coronary artery disease also have a chronically blocked artery.
Without treatment a CTO can lead to:
⦁ Chest pain (called angina)
⦁ Shortness of breath
⦁ Fatigue
⦁ Inability to participate in many normal daily activities

Risk Factors
Ciggerate Smoking

Symptoms
Acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)

Diagnosis
Obstructive coronary artery disease
Pathophysiology
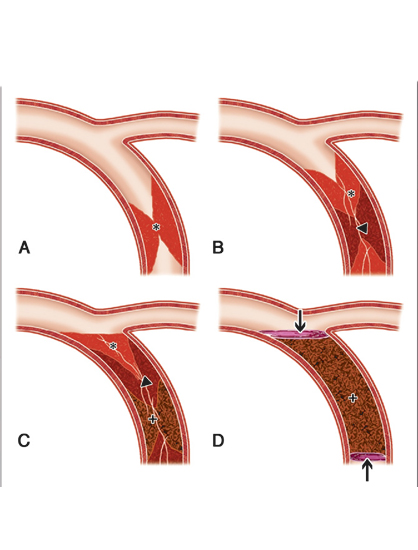
Pathogenesis of coronary artery disease which can progress to CTO lesions, has multiple contributing factors, which include upregulation of the immunologic and inflammatory markers (cytokines, leukocytes, high sensitivity C-reactive protein), endothelial dysfunction, and cholesterol accumulation. Most commonly, it starts with the collection of smooth muscle cells within the intima, and this progresses to macrophages accumulating in the intima leading to pathologic intimal thickening and progression of lesions.
CTO PCI Procedure
- Most patients with a symptomatic total coronary occlusion traditionally required coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery to treat the blockage.
- Total blockages of the coronary artery have historically been the most challenging types of blockages to treat with an interventional procedure.
- New technology and new percutaneous techniques to treat total coronary occlusions allow experienced physicians to considerably improve the success rate of this treatment approach, making it a viable treatment option for patients who are experiencing symptoms related to these blockages.
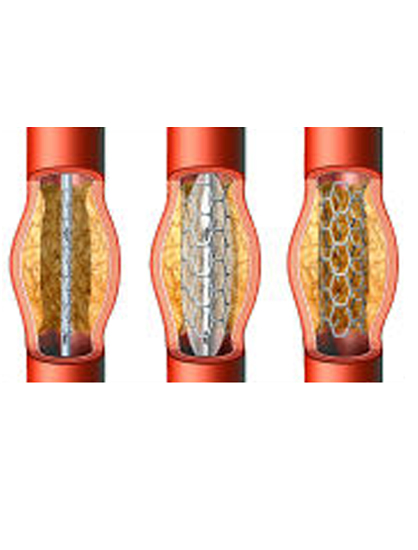
- Calcification within a chronic total occlusion (CTO) is an independent predictor of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) failure, prolonged procedure duration, suboptimal stent expansion, and complications and thus is a key characteristic in CTO complexity scores.
- CTO can be crossed by luminal tracking (“intraplaque”) or by dissecting around the occlusion and through the less resistant subintimal space (“extraplaque”).
- This can be done antegradely (antegrade wiring (AW) or antegrade dissection re-entry (ADR)) or re Calcium modification is required more often if the course is intraplaque. (Retrograde wiring (RW) or retrograde dissection re-entry (RDR)).
- While the morphology of plaque calcium can be concentric, eccentric, or nodular, extraplaque tracking and displacement of the plaque and lumen can result in the formation of a calcified “pseudonodule.
- Calcium modification is frequently performed during CTO PCI using scoring (SB), cutting (CB), and high-pressure (OPN) balloons or rotational (RA), orbital or laser atherectomy.
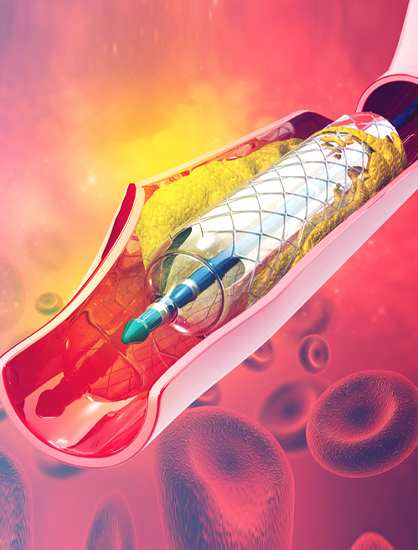
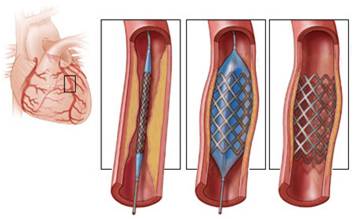
During the procedure
- At the start of the procedure patients receive sedation.
- During the procedure, two catheters are placed in arteries (leg or wrist) to allow the ability to go forwards or backwards as needed.
- Cardiac interventionist are now using special guide wires and catheters that are gently steered across the total blockages.
- The fine movement of the guide wire tip is much easier to control than previous guide wire tips.
- In addition, at a very few centers in the United States, including the Cleveland Clinic, physicians use the “retrograde” approach, in which total coronary blockages are accessed from collateral blood vessels.
- Collateral blood vessels are new blood vessels that form to reroute blood flow around a blockage and develop when the severity of a blockage increases.
- During the procedure the patient is awakened and speak to doctor if having any discomforts during procedure.
- The procedure takes approximately 3-4 hours.
- First-time success rates approach 85-90%.
- In some cases, partial success occurs, and patients will be recommended to have a re-attempt 6-8 weeks later.
- Most patients are discharged the next day after review of their catheter sites and blood work.
Results
- Patients who undergo CTO PCI often have an improvement of their symptoms within days to weeks.
- Some patients notice an improvement even before discharge.
- Studies have shown that patients who have had CTO PCI have seen an improvement in their quality of life including:
- Reduced chest pain (angina)
- Reduced shortness of breath
- Increase in physical activity
- Decrease in feelings of depression
- Higher levels of energy
- The Mass General CTO PCI team will arrange for post-procedure follow-up.
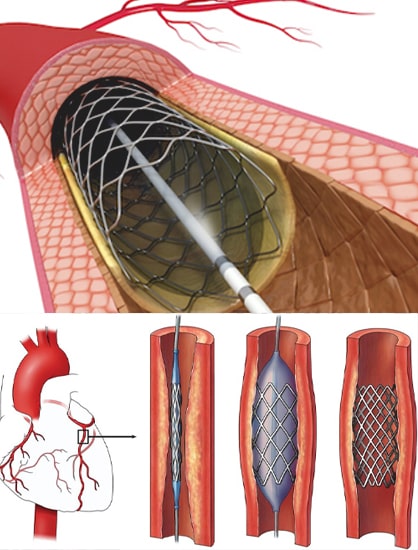
Success Rate
- 60-90% centers in experienced
- The retrograde approach is not without potential complications, but the complication rate is only slightly higher than standard angioplasty, depending on the circumstances.
- Each patient is evaluated to see what treatment options is best, based on the type of cardiovascular disease, the location of disease, patient’s age and co-existing medical conditions
Patient Education
Contact doctor if you experience
- Do not lift heavy weights
- Quit smoking
- Take healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Maintain healthy weight

