Calcification is a buildup of calcium in body tissue. The buildup can form hardened deposits in soft tissues, arteries, and other areas. Calcium is transported through the bloodstream. It’s also found in every cell. Some calcifications don’t cause painful symptoms, while others can lead to serious complications. Treatment depends on the location, severity, and underlying cause of the deposits.
According to the National Academy of Medicine, about 99 percent of your body’s calcium is in your teeth and bones. The other 1 percent is in the blood, muscles, fluid outside the cells, and other body tissues.
Arterial
calcification
- Artery calcification starts at a young age over 40 years of age
- People with coronary artery disease will have calcification of the blood vessels
- 90% of men and 67% of women over 70 years of age have coronary artery calcifications
Calcification in the arteries that supply blood to the heart increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. It can affect:
- Blood flow through the heart
- How the arteries contract and dilate to alter the flow of blood
- How well the arteries react to changes in blood flow
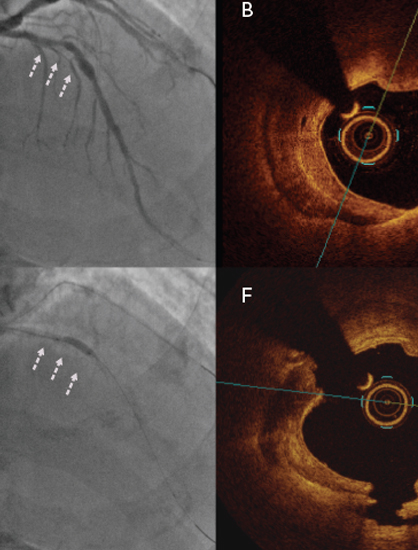
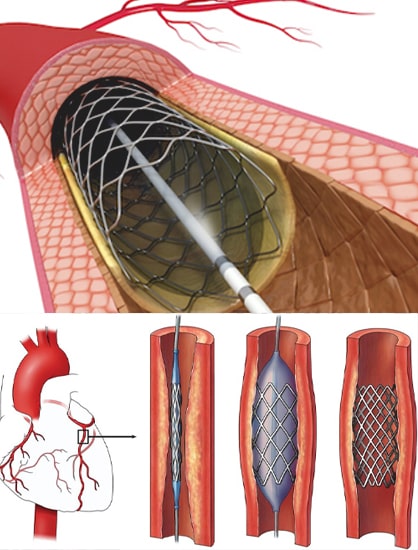

Symptoms
Artery calcification has no typical symptoms but may present as:

Causes
Metabolic syndrome


