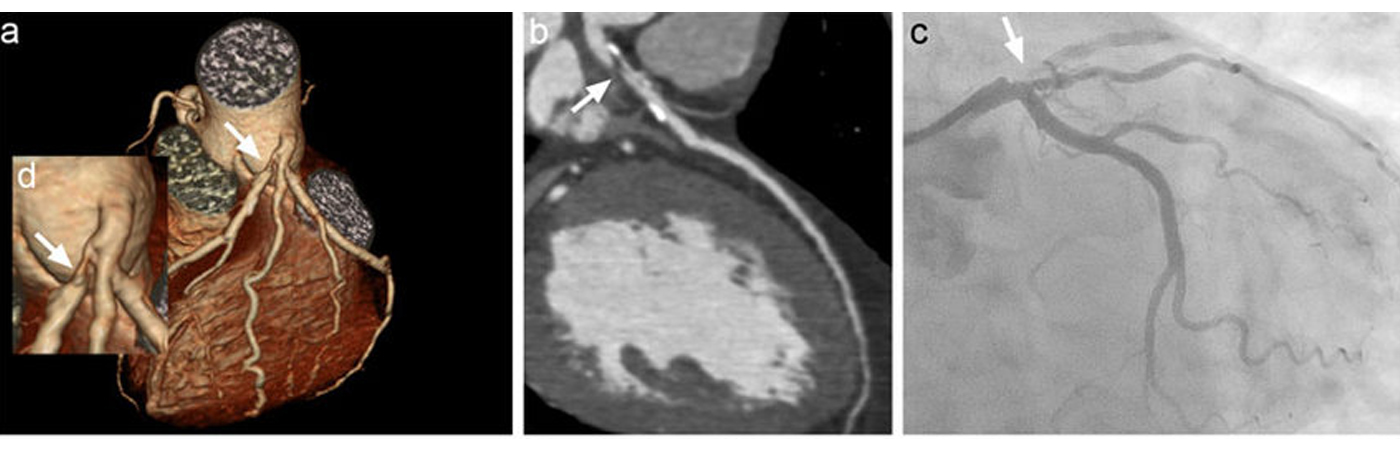
Computed tomography (CT) coronary angiogram is an effective imaging test used to identify the plaque depositions in the arteries associated with the heart. This imaging test does not use any type of catheter insertion to the heart. The CT coronary angiogram uses the powerful X-ray equipment to produce pictures of the blood vessels and the heart. This technique is very safe and noninvasive.
CT coronary angiogram is a very effective way to identify various heart problems at an early stage. It is useful, especially, to diagnose atherosclerosis, even before any symptoms are observed. Plaque is made of various substances such as fat, cholesterol and calcium that deposit along the inner lining of the arteries that reduce or completely block blood flow.
Patients undergoing this scan receive an iodine-containing contrast material as an intravenous (IV) injection to ensure the best possible images of the heart blood vessels. The images generated during a CT scan can be reformatted to create three-dimensional (3D) images that may be viewed on a monitor, printed on film or by a 3D printer, or transferred to electronic media.

CT angiogram is advised by the doctor to identify the following problems:

Risks

Side Effects
Procedure
Before the procedure
- Avoid eating at least 4 hours before the procedure
- Avoid taking caffeine-induced beverages
- Drinking water is allowed
- Remove the metal objects that interfere with the procedure
- Inform the doctor about past medical, medication, and allergic history
- Inform current medications
- If you are diabetic, ask the doctor if insulin to be taken before the procedure or not
- The vital signs of the patient, i.e., pulse rate, body temperature, blood pressure, oxygen levels or breathing rate, are checked before the coronary angiogram.
- Empty the urinary bladder before the procedure
During the procedure
- CT coronary angiogram is usually performed in the outpatient facility or the Radiology department.
- The patient is asked to lie down on a padded table, which slides into a big, hollow, circular machine (donut-like)
- To examine the heart carefully, the doctor gives some medications like the beta blockers to the patient. These medicines slow down the heart rate of the patient for some time.
- The heart rate and rhythm are monitored continuously during the procedure with the help of electrodes attached to the patient’s body
- The doctor will then clean the area (arm or hand), from where the contrast or special dye is inserted
- The dye is administered intravenously (IV), in order to highlight the arteries of the heart and enable the doctor to detect the problem areas carefully. Before inserting the contrast, the doctor gives local anesthesia to numb the area.
- This procedure takes approximately one hour
- The X-ray machine will then take images of the patient from various angles
- The patient is advised not to move during the procedure and to hold the breath at times, in order to get clear images.
After the procedure
- Electrodes are removed from the patient’s body
- There is no need of hospitalization because the procedure is non-invasive
- The patient is capable to drive back to home without any help
- The patient is advised to take lot of fluids to flush out the dye completely from the body
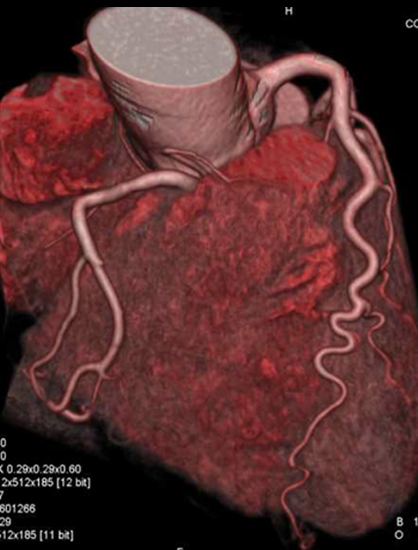

Results
Findings, if the report is abnormal
- Plaque formations or atherosclerosis
- Reduction in the amount of blood flow through the arteries
- Reduced flow of blood to the heart and various surrounding blood vessels
- Any abnormality in the overall condition and structure of the heart e.g. congenital heart diseases
If the report is normal
- There is no abnormality detected
- The heart is healthy and fit
- No obstructions or blockages are observed
- The structure of the heart is normal
Lifestyle modifications
- Avoid smoking and alcohol
- Eat healthy and nutritious food
- Keep the weight in control
- Avoid eating saturated food
- Manage stress effectively
- Regular exercise
- Interventional or surgical heart procedure may be advised


