Fractional Flow Reserve
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is a technique used in coronary catheterization to measure pressure differences across a coronary artery stenosis to determine if stenosis impedes oxygen delivery to the heart muscle.
Indications:
- Multivessel disease
- Acute coronary syndrome
- Left main lesions
- Bifurcations
- Bypass grafts
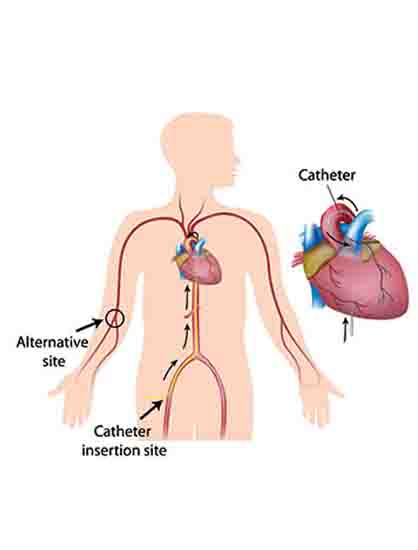
During coronary catherization
- A catheter is inserted into the femoral or radial arteries
- A sheath and guidewire
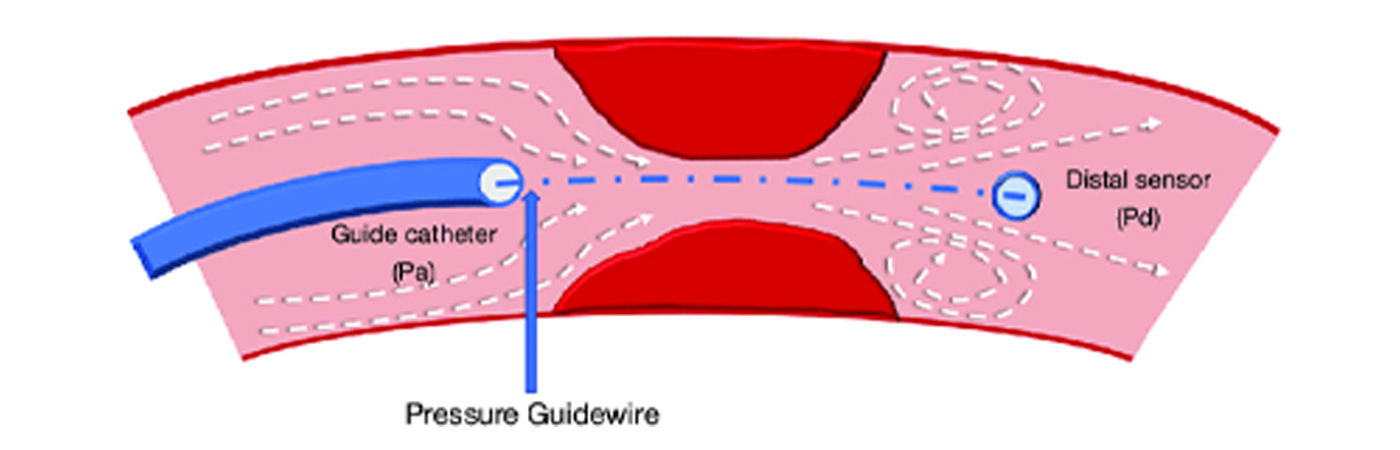
- FFR uses a small sensor on the tip of the wire
- To measure pressure, temperature and flow
- Which determines the exact severity of the lesion
- Done during maximal blood flow
- Induced by products such as adenosine or papaverine
- Wire is pulled back
- Pressures recorded across the vessel
Equation
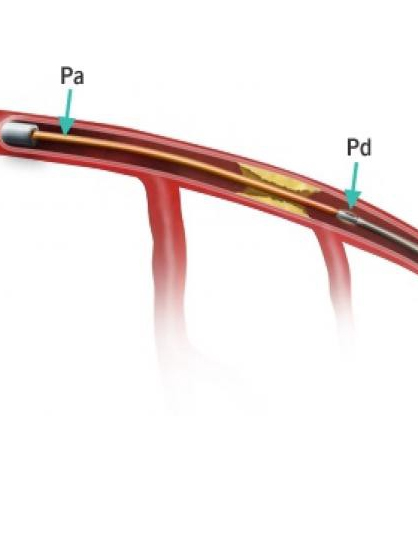
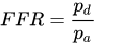 FFR is the ratio of maximum blood flow distal to a stenotic lesion to normal maximum flow in the same vessel. It is calculated using the pressure ratio. Where,
FFR is the ratio of maximum blood flow distal to a stenotic lesion to normal maximum flow in the same vessel. It is calculated using the pressure ratio. Where,
Pd = Pressure distal to the lesion
Pa = Pressure proximal to the lesion
Equipment
- Guiding catheter
- Pressure monitoring guidewire
- Hyperemic stimulus
- Vasodilation administration – to achieve maximal hyperemia of coronary artery
Complications: Rare
- Transient bradycardia (1.7%)
- Coronary spasm (2%)
- Ventricular fibrillation (0.2%)
- Vessel trauma

