Advanced Imaging
Cardiac imaging is a subspecialty of diagnostic radiology. A cardiac radiologist supervises or performs and then interprets medical images to diagnose diseases of the heart such as heart disease, leaky heart valves and defects in the size and shape of the heart.
A physician may recommend cardiac imaging to support a diagnosis of a heart condition.
Options
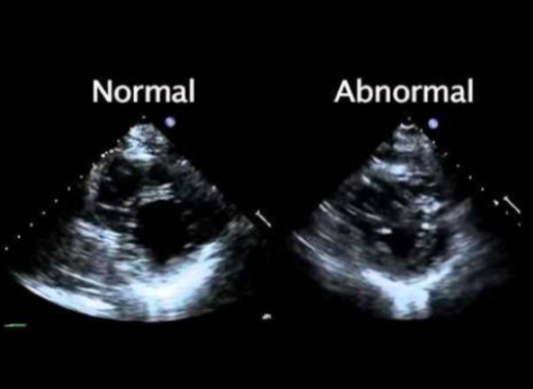
Echocardiography
An echocardiogram (echo) is a graphic outline of the heart's movement.
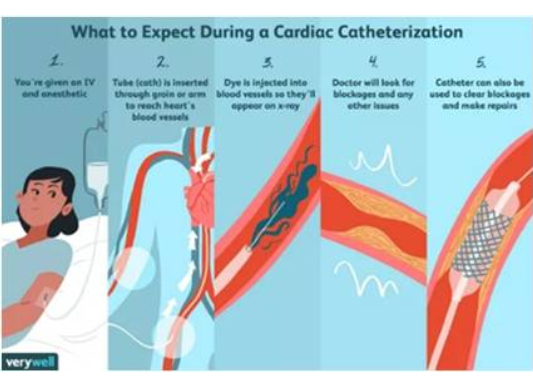
Cardiac Catherization/Angiogram
It is an invasive procedure, where a thin, long, flexible tube is inserted, via the arm or groin, and is guided to the blood vessels of your heart to evaluate and treat heart conditions.
CT Angiogram
It combines a CT scan with an injection of a special dye to produce pictures of blood vessels and tissues in a part of your body.
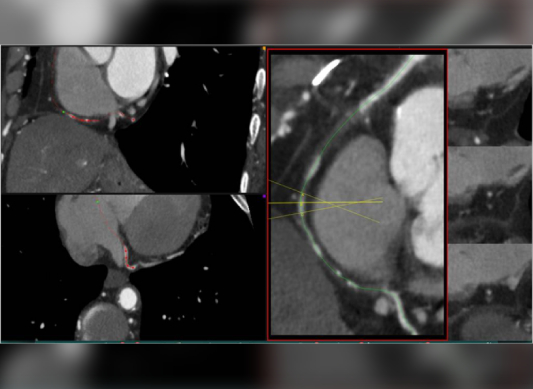
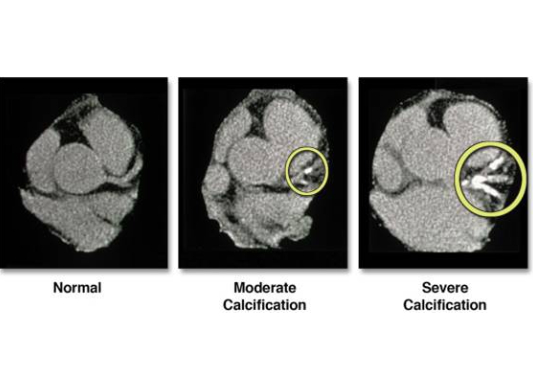
CAC Scanning
Measures the amount of calcium in the walls of the heart's arteries.
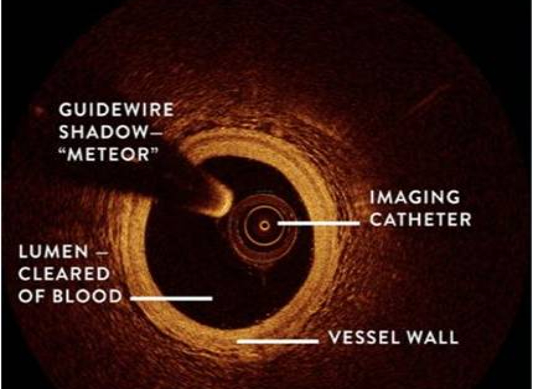
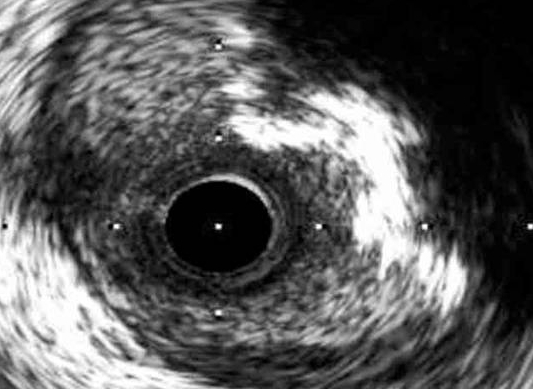
INTRAVASCULAR ULTRASOUND (IVUS)
Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) is a medical imaging methodology, which uses an ultrasound probe that is inserted to the artery like a regular angioplasty catheter to provide an image from within the artery. Used to see the inside blood vessels using soundwaves. A computer produces pictures of soft tissues.
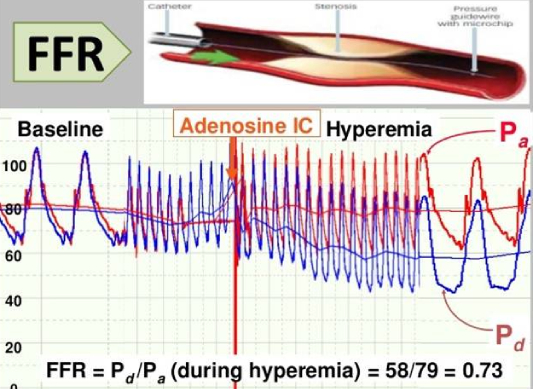
Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR)
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is a technique used in coronary catheterization to measure pressure differences across a coronary artery stenosis to determine if stenosis impedes oxygen delivery to the heart muscle.
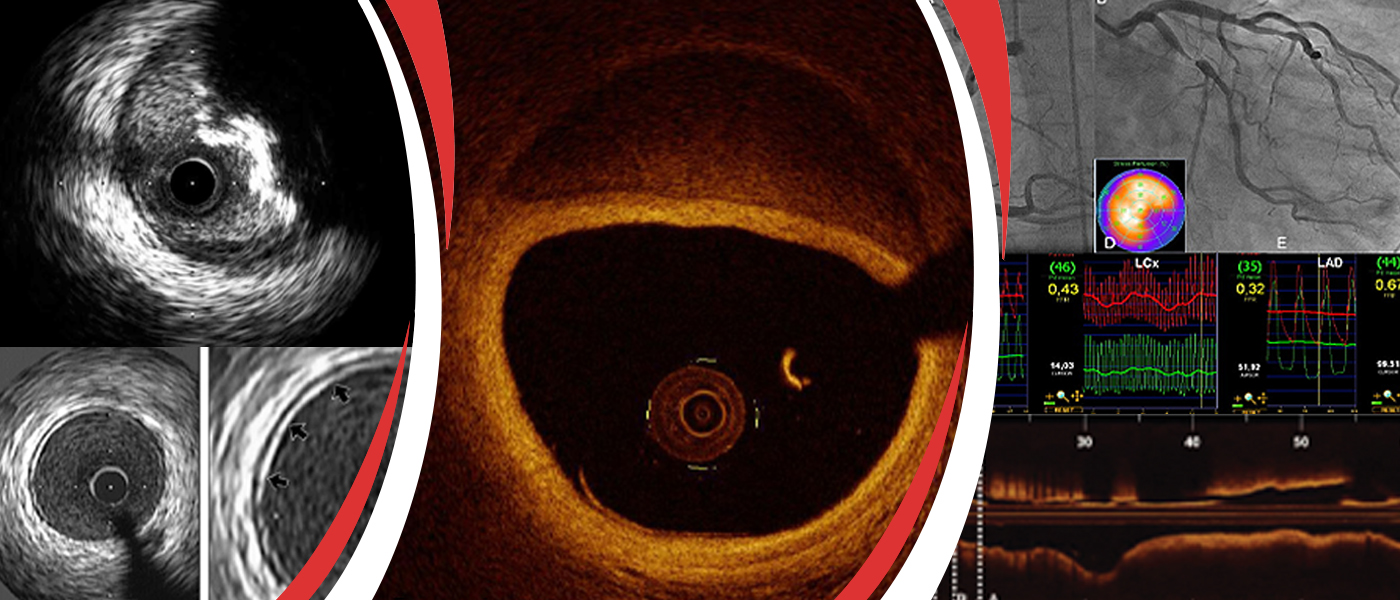
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a diagnostic procedure that uses near-infrared light to create images of the inside of the coronary arteries. The technique delivers very high-resolution images.